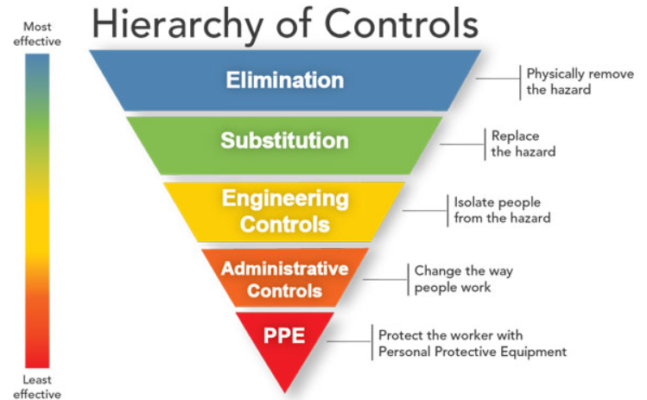
Controlling exposures to occupational hazards is the fundamental method of protecting workers. The pyramid below highlights a Hierarchy of Controls, which shows the most effective to least effective control methods in reducing workplace injuries.
Elimination and Substitution
Elimination and substitution, while most effective at reducing hazards, also tend to be the most difficult to implement in an existing process. If the process is still at the design or development stage, elimination and substitution of hazards may be inexpensive and simple to implement. For an existing process, major changes in equipment and procedures may be required to eliminate or substitute for a hazard.
Engineering Controls
Engineering controls are favored over administrative and personal protective equipment (PPE) for controlling existing worker exposures in the workplace because they are designed to remove the hazard at the source, before it comes in contact with the worker. Well-designed engineering controls can be highly effective in protecting workers and will typically be independent of worker interactions to provide this high level of protection. The initial cost of engineering controls can be higher than the cost of administrative controls or PPE, but over the longer term, operating costs are frequently lower, and in some instances, can provide a cost savings in other areas of the process.
Administrative Controls and PPE
Administrative controls and PPE are frequently used with existing processes where hazards are not particularly well controlled. Administrative controls and PPE programs may be relatively inexpensive to establish but, over the long term, can be very costly to sustain. These methods for protecting workers have also proven to be less effective than other measures, requiring significant effort by the affected workers.
Recent Posts
The U.S. Department of Labor Announces Proposed Rule To Protect Indoor, Outdoor Workers From Extreme Heat
The U.S. Department of Labor has proposed a new rule aimed at protecting workers from extreme heat hazards. This initiative seeks to safeguard approximately 36 [...]
Supreme Court Overturns Chevron Deference: What It Means for Workplace Safety and Regulation
The landscape of federal regulation is set for a seismic shift following a recent Supreme Court decision. On June 28, in Loper Bright Enterprises, et [...]
Navigating the Compliance Maze: How NARFA Simplifies Employee Benefits for Automotive and Trade Industries
In today's complex regulatory environment, businesses in the automotive, roads, fuel, and related industries face unprecedented challenges in managing employee benefits. Recent studies show that [...]