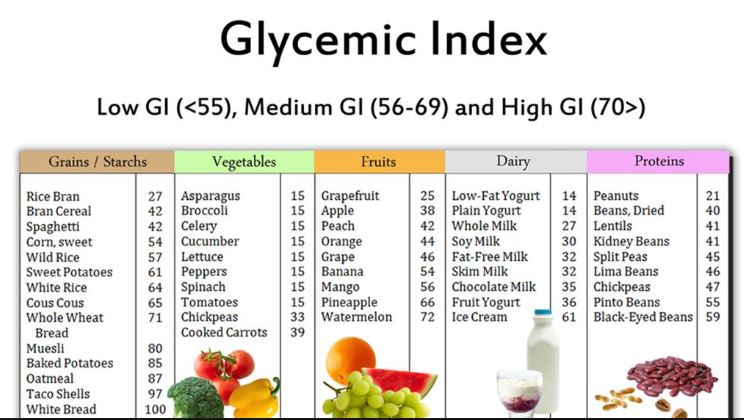
Let’s start with how to pronounce this big word first. Gly-see-mik. It relates to the sugar (glucose) level in your blood. The glycemic index (GI) measures how high and how fast your blood sugar spikes after you eat a specific type and amount of food compared to consuming the same amount of pure sugar. The carbohydrates in some foods (high GI foods), like white rice, bread and potatoes, can spike blood sugar higher and faster like sugar, whereas lower glycemic foods, like nuts, lentils and broccoli, have a slower, steadier effect. If a food has a 35 percent GI, like a serving of kidney beans, it means it boosts blood sugar only 35 percent as much as pure sugar does. Another food may have a 90 percent GI, like a serving of a flavored sports drink, which is high enough to act like pure sugar in the bloodstream.
Why GI matters
Left unchecked, high blood sugar can lead to serious health concerns like diabetes, heart disease and some cancers. Eating foods with low GI values can mean a slower rise in blood sugar, and help you control your weight and maintain better health. Foods with a lower GI value can help curb cravings for unhealthy foods and keep you feeling satisfied longer. If you are concerned about a health issue and how to prevent or manage it, work with your doctor on the right eating plan for you.
Recent Posts
The U.S. Department of Labor Announces Proposed Rule To Protect Indoor, Outdoor Workers From Extreme Heat
The U.S. Department of Labor has proposed a new rule aimed at protecting workers from extreme heat hazards. This initiative seeks to safeguard approximately 36 [...]
Supreme Court Overturns Chevron Deference: What It Means for Workplace Safety and Regulation
The landscape of federal regulation is set for a seismic shift following a recent Supreme Court decision. On June 28, in Loper Bright Enterprises, et [...]
Navigating the Compliance Maze: How NARFA Simplifies Employee Benefits for Automotive and Trade Industries
In today's complex regulatory environment, businesses in the automotive, roads, fuel, and related industries face unprecedented challenges in managing employee benefits. Recent studies show that [...]




